Standard cDNA library
cDNA libraries are produced using our proprietary technology, which features full-length-enriched, high quality size-fractionated, and directionally cloned cDNA. For information on normalized cDNA libraries, please click here.
Related services
- Library pooling and amplification is available in liquid or semi-solid medium.
- Duo-range libraries feature for an additional: Receive 2 sub-libraries of totaling 1.5 million clones.
- Each will have a different insert size range of your choice (ex: 500bp-2Kb and 2Kb-4Kb). This maximizes flexibility and representability.
- Arraying is available for an additional fee.
Highlights
- cDNA synthesis to obtain full-length-enriched cDNAs.
- Cloning will be directional.
- Size fractionation and ligation to vector (modified pBluescript).
- Transformation in E. coli DH10B.
- More than 99% recombinants.
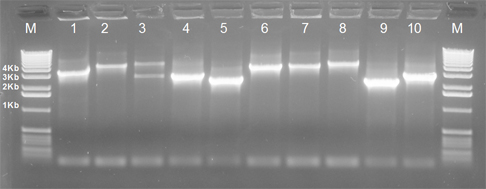
- Testing of 10 clones for insert size determination (gel picture will be provided).
Image 1: Insert size determination
Normalized cDNA library
cDNA libraries are produced using our proprietary technology, which features full-length-enriched high quality size-fractionated, and directionally cloned cDNA.
Related Services
- Library pooling and amplification is available in liquid or semi-solid medium.
- Duo-range libraries feature for an additional fee: Receive 2 sub-libraries of totaling 1.5 million clones.
- Each will have a different insert size range of your choice (ex: 500bp-2Kb and 2Kb-4Kb). This maximizes flexibility and representability.
- Arraying is available for an additional fee.
Highlights
- Representation of abundant transcripts greatly decreased (see Figure 1). Reduction of abundant transcripts is essential for discovery of rare transcripts. For a non-normalized cDNA library, usually 10–20 abundant genes account for at least 20% of the cellular mRNA mass; several hundred genes of medium abundance genes comprise 40–60% of the mRNA mass; several thousand rare genes (<10 mRNA copies per cell) may account for 20–40% of the mRNA mass. Hence, random sequencing of clones from non-normalized cDNA libraries is inefficient, and very costly, for discovering rare transcripts. Decreasing the percentage of these transcripts before sequencing significantly increases the chance for rare gene discovery.
- cDNA normalization efficiency is strictly monitored. Apart from the normalization of cDNA population, a parallel normalization is performed. In the parallel normalization, a reporter gene is added to the cDNA population before normalization, as a control. The percentage of this control gene can be easily tested before and after normalization to ensure the quality of normalization. The enrichment of rare and unique sequences is accomplished by using our controlled normalization procedure that reduces the frequency of abundant sequences as much as 400 fold.
- Our Normalized cDNA molecules are longer (See Figure 2). Our normalization hybridization method prevents significant loss of average insert size. We perform normalization of cDNA population prior to cloning and library preparation. This prevents size bias against long and otherwise difficult-to-amplify cDNA due to clone bias.
- Normalized cDNA molecules are full-length-enriched. We use proprietary method to synthesize full-length enriched cDNA for normalization. DNA libraries rich in clones containing complete coding sequences with 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) for each transcript in a single cloning step are invaluable for high-throughput transcriptome analysis.
- Normalized cDNA molecules are directionally cloned. Directional cloning facilitates bi-directional sequencing, PCR screening and expression.
- Low vector background. Bio S&T uses efficient ligation, a high quality vector, as well as electroporation for cloning. As much as 99% of clones have inserts.
Figure 1: Reduction in abundant transcripts after normalization.
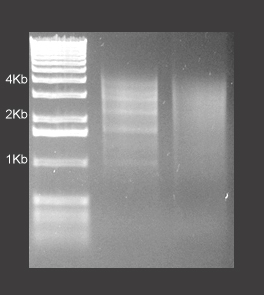
Figure 2: Insert size determination of a normalized library.

Please note the absence of the redundant bands following the normalization procedure as well as the large size of the cDNAs.

