We have been constructing high-quality cDNA and DNA libraries since 1997. We have tremendous experience with plant, animal, yeast and bacterial genomic BAC library construction. Some of our clients include Agriculture Canada, Pioneer Hi-Bred Int'l (DuPont), Bayer, Cargill and the Max Planck Institutes in Germany. We guarantee a quick turnaround-time, unbeatable pricing and large inserts.
References are proudly provided.
An arrayed or non-arrayed BAC library (once arrayed by client) is the preferred choice for researchers wishing to screen for BAC clones using hybridization techniques. An arrayed library is also the only template that will do for whole genome sequencing or physical mapping.
We also offer BAC library construction in custom and shuttle vectors! Please contact areti@biost.com
Are you planning on screening only for a few target clones? Please visit our Screened BAC library section with your vector of choice for evaluation.
Highlights
- We typically construct a minimum 5X BAC library which provides a 99.3% probability of finding the target sequence. Additional coverage and 2-enzyme digestion is available (additional fee). We pride ourselves in tailoring our services to suit our client's needs.
- Coverage is guaranteed. Amount of clones received is based on a guaranteed coverage and 120Kb average insert size.
- HMW DNA isolation and QC by HMW DNA enzymatic digestion are included.
Delivrables
ARRAYED BAC LIBRARY CONSTRUCTION (WITH CLONE PICK-UP)
- Clones will be arrayed and amplified in 384-well plates (1 unique clone/well), and shipped on dry ice.
- Genomic coverage is guaranteed.
- Plates will be identified with bar-coded labels.
NON-ARRAYED BAC LIBRARY CONSTRUCTION (WITHOUT CLONE PICK-UP)
- Genomic coverage is guaranteed
- Client will receive BAC clone mixtures (transformed E. coli cells containing BAC DNA) stored in glycerol and shipped on dry ice.
- An additional 5% of clones will be shipped at no extra charge to compensate for loss of titer during delivery.
- This option is recommended to scientists studying large genomes and/or having arraying capabilities and/or wishing to limit shipping fees.
Related services
- Nylon filters: Available in small (8x12cm; maximum 3,072 clones) and large size (22.5x22.5cm; maximum 18,432 clones). Minimum order is 3 sets. The nylon filters will be ready for hybridization with the clones, in duplicate, cross-linked to them (Amersham Hybond-N+).
- BAC library copy: Available for the arrayed BAC library option only. A copy of the Master BAC library can be made and stored or shipped.
-
NEW Super pools and Pools Package derived from Arrayed BAC library: We can also provide the following pools which will allow client to immediately begin screening.
- Plate Pools
- Superpools
- Row pools from Superpool plates
- Column pools from Superpool plates
Our strengths
- We guarantee coverage.
- High average insert and even insert size distribution (see Graph 1 below).
- We perform HMW DNA extraction at our facilities.
- We have experience with plant, fungal, bacterial and animal libraries.
- We have extensive experience with GC-rich organisms and marine bacteria.
- Our arrayed BAC libraries are shipped in bar-coded microplates.
- We have extensive experience shipping worldwide.
- Shipment temperature of non-arrayed libraries is always monitored using a BLUE FLAG Temperature Data logger.
- We provide technical support.
- BAC libraries are the client's property and are never used internally, sold or distributed.
- We provide references
Table 1: A few libraries constructed in the past with obtained average insert sizes.
| Starting material | Insert size |
| Musmusculus | 180 Kb |
| Zea mays | 150 Kb |
| P. brassicacearum | 160 Kb |
| P. omnivore | 185 Kb |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | 150 Kb |
| Homo sapiens | 215 Kb |
Figure 1: PFG following NotI digestion of insect BAC clones ( Mamestra configurata ) with an average insert size of 178Kb
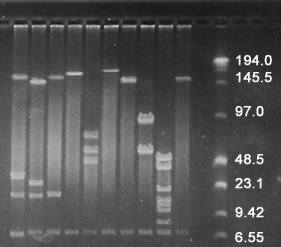
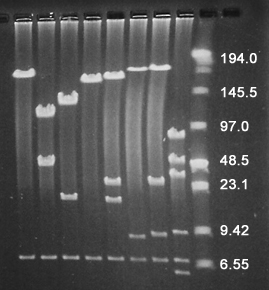
Figure 2: PFG following NotI digestion of fungal BAC clones P. omnivora) with an average insert size of 185Kb.
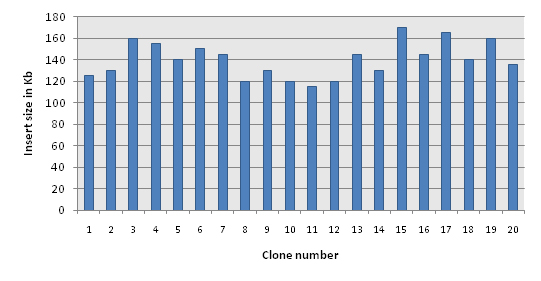
Graph 1: BAC clone insert size distribution (average of 140Kb) of a Soybean BAC library (Glycine max).
Scholar articles for BAC library construction
- https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms4706?message-global=remove
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00122-016-2740-0
- https://bmcplantbiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12870-019-1766-2
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0197458014008252
- https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2164-12-217
- https://nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04128.x
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11248-012-9646-7
- https://academic.oup.com/gbe/article/doi/10.1093/gbe/evq047/577231
Importance of a BAC library
BAC libraries are essential elements in doing large-scale genome research such as screening for genes of target, biosynthetic gene cluster cloning, transgene identification, gene/gene cluster functional analyses, physical mapping and genome sequencing. Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) cloning technology was developed in the early 1990s and quickly gained popularity among scientists whose requirement included developing a thorough understanding of gene network topology based effects, with particular emphasis on gene dosage and gene cassette orientation. Although this technology was developed much later than Yeast Artificial Chromosome (YAC) and cosmid/fosmid based genome library cloning technologies it soon became popular and tractable because of the technical advantages offered by BAC based cloning over YAC and cosmid/fosmid library cloning systems:1. Larger insert sizes (>100 kb).
- Larger insert sizes (>100 kb).
- More stable than YAC clones. YAC clones can be unstable and un-clonable.
- BAC DNA can be easily isolated (supercoiled BAC DNA versus linear YAC DNA).
The other important applications of BAC library construction are in large-scale physical mapping and genomic sequencing. Here are some examples of its major applications:
Library screening
BAC libraries enable rapid screening and isolation of target BAC clones.
Isolation of gene clusters for biosynthetic pathways
A BAC library can be used to screen for gene pathways in microorganisms derived from soil and marine environments. This enables discovery of new compounds in drug discovery (mainly antibiotics), plant genetics and microbial metabolic research. Finding novel enzymes is another application that is important to the industrial microbiology sector.
Preparation of FISH probes
FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization) probes are commonly made from BAC clones. This technique is useful in the detection of chromosomal rearrangements, deletions and aneusomies.
Complementation for map-based gene cloning using binary vector in plants
A BAC library can be used to interrogate the genetic structure of plant genomes as well as mutant genotype analysis using complementation techniques. This endows the scientist with a reliable tool to study global gene expression in plant species and to isolate individual genes.
Physical maps and complete genome sequencing
BAC libraries and isolated overlapping BAC clones are important tools for genome sequencing and contig assembly.